licesnse_checker_3
Name: licesnse_checker_3
Author: pourmeadrinkwhileimfloating
URL: https://crackmes.one/crackme/62327b0433c5d46c8bcc0335
Download: here
Difficulty: 1
Quality: 1
Goal: write a key generator
Method: static analysis
Tools used: Ghidra
Executable format: ELF
Arch: x86-64
MD5: 792dff81ac2d2b3e3d3e6c094fc0f1e5
SHA256: 29412589df288184ca00159c8275e8218a5d103899cf63954edd97b6c931c2eb
Tutorial
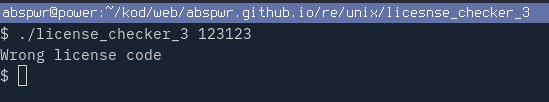
Run the crackme with ./license_checker_3 123123 and enter random input
Ghidra
Open Decompile window with CTRL+E shortcut.
key check is performed in main function.
Rename variables to make analysis easier. Right click on variable and change its name accordingly.
So it makes more sense, like bellow.

Immediately, we can see that key check is performed in single while loop in main.
Loop is executed len times depending on number of characters in a string we passed via argv[1].
Each of single characters is converted to an int value via atoi function and it’s added to sum variable.
After the loop finishes, sum variable is compared to 0x32 value (dec. 50), and if it’s true, good boy message is printed.
There is no restriction to length of passed string, so we both 5555555555 and 8888855 are valid keys, since they both add up to 50.
atoi function returns 0 for a nonnumeric character, so the key 88a88.8x55 will work as well.
Naive brute-force key generator can be found here.
// abspwr
package main
import (
"fmt"
"math"
)
func sumDigs(n uint64) uint64 {
if n == 0 {
return 0
} else {
return n%10 + sumDigs(n/10)
}
}
func printDigs(n uint64) {
if n == 0 {
fmt.Println()
} else {
printDigs(n / 10)
fmt.Print(n % 10)
}
}
func main() {
n := 6
t := uint64(0x32) // 50
max := uint64(math.Pow10(n))
i := uint64(0)
for i = 1; i < max; i++ {
if sumDigs(i) == t {
printDigs(i)
}
}
}